Embedded Programming for the Internet of Things
Embedded Programming for the Internet of Things
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Sciforce
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



Embedded programming has a long history of making devices do what people need. However, it remains largely overshadowed by application programming. When application programmers were embracing relatively high-level object-oriented languages like C++ or Java, or graphical application development environments like MATLAB, embedded programmers were only moving from into C. They were always outnumbered by app programmers. Today, even hobbyists can develop an app using an easy language and share it with the world, while embedded programmers need to have deep knowledge of hardware and firmware, and how to write programs that can execute in often highly resource-constrained environments. With the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), the balance can finally shift. Now that many new thermostats, toasters, watches and light bulbs are equipped with processors and connectivity, the market needs more embedded programmers to program these devices and simpler tools to allow these programmers to write code without plunging into the low-level hardware.
What Is Embedded Programming?
Techopedia offers a definition of embedded programming is "a specific type of programming that supports the creation of consumer-facing or business facing devices that don't operate on traditional operating systems the way that full-scale laptop computers and mobile devices do." The idea of embedded programming is part of what drives the evolution of digital appliances and equipment in today's IT markets.
In simpler words, embedded programming is designing and writing programs for small "computers" that are embedded within devices other than traditional PCs, laptops or smartphones. It's that which enables microcontrollers to awaken previously "dumb" devices—e.g. thermostats, lighting systems, parking meters, etc.—and give them some ability to "reason" about their environment.
Embedded Programming and IoT
From an engineering perspective, the Internet of Things describes a network of embedded, microprocessor-controlled devices, where that network is connected directly or indirectly to the web. The three pillars of IoT are, therefore:
- Embedded programming
- Network technology
- Information technology
IoT is soon to be everywhere. Embedded devices are, therefore, soon to be ubiquitous as well.
Here is a brief glance at some of the ways in which IoT is changing industries:
- Industry — Industrial machinery and control, temperature monitoring and cognitive anomaly detection.
- Healthcare — Blood pressure monitors, heartbeat monitors, fitness trackers, embedded medication delivery.
- Aerospace and Defense — Flight control systems, actuation, air and thermal management, engine power monitoring and control.
- Smart Homes — Home security systems, digital cameras, televisions and kitchen appliances.
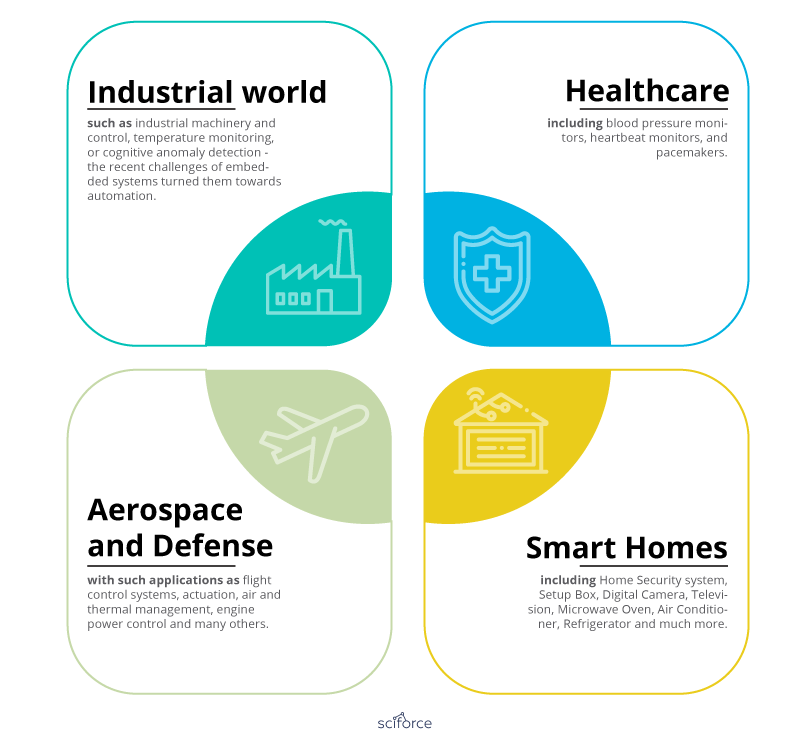
Image Credit: Sciforce
Diving Into Embedded Systems
Some say that every complex system in the world can be reduced to two conceptual spheres: software and hardware. An embedded system represents, more or less, the intersection of those spheres: hardware and software.
Exploring Embedded Hardware
A typical embedded development board is divided into five "modules": the processor, memory, input devices, output devices and bus controllers.
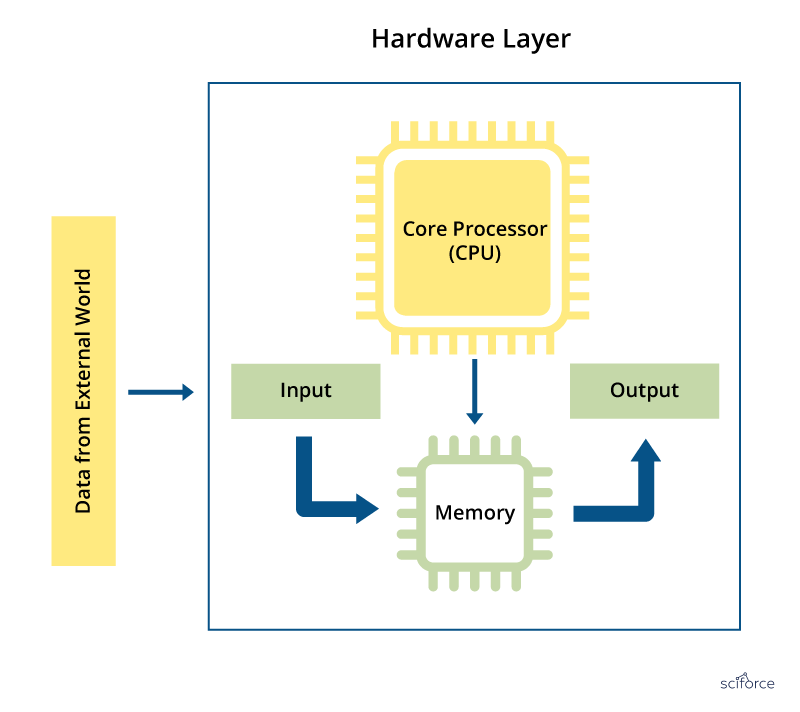
Image Credit: Sciforce
embedded programming is essential to the way IoT devices work. For production, you'll need C/C++ and some hands-on electronics experience.
Hardware Components of an Embedded System
Processor
Embedded processors can be broken down into two categories: ordinary microprocessors that use separate integrated circuits for memory and peripherals, and microcontrollers that have on-chip peripherals, reducing power consumption, size and cost. Some examples of these include:
- Microcontroller (CPU) — an intelligent device that computes the tasks assigned by the user and is used to build small applications with precise calculations.
- System on Chip (SoC) — comprises a CPU, peripheral devices (timers, counters, etc), Communication interfaces (I²C, SPI, UART), and power management circuits on a single integrated circuit.
- ASIC processor (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) — designed for a specific application by a company or manufacturer.
- DSP processor — removes the noise and improves signal quality in audio and video applications.
Memory
Memory is used to store data that's being used on the device. Some examples of the types of memory used in embedded systems include Non-Volatile RAM (Random Access Memory), Volatile RAM, DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), etc.
Input Devices
Input devices, such as sensors, switches, photodiode, optocouplers, etc., capture data from the outside world to be processed or exported from the device.
Output Devices
Output devices, including LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) or LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays, seven segment displays, buzzers and relays, respond to input events from outside the microcontroller.
Bus Controllers
The bus controller is a communication device that transfers data between the components inside an embedded system. The most widely used bus controllers are serial buses (I2C, SPI, SMBus, etc.), RS232, RS485 and Universal Serial Bus (USB).
Exploring Embedded Software
Embedded software, sometimes called firmware, is written for the device drivers, operating system and applications, as well as for error handling and debugging.
<!-- wp:heading --> <h2 class=" />Software Components of an Embedded System
Device Driver
A device driver is a piece of embedded code written for a specific piece of hardware.
Operating System (OS) or MicroOS
Embedded systems have a range of operating systems, including RTOS (Real-time Operating Systems), mobile embedded, stand-alone and network embedded systems.
Most of the embedded software is now written in two languages: C and C++. There isn't much of a difference between C and C++ in terms of syntax. However, C++ has some additional features, like enhanced security and closeness to real-world applications, while C is considered more reliable and has better performance by directly interacting with the hardware.
Key Considerations When Creating an Embedded Product
The best way to start writing software that would directly affect physical objects is to explore embedded platforms like the Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or Particle.
To develop a viable product you should take the following steps:
Step 1. Learn C or C++
This is where many stop since these languages can be hard to learn. However, if you want to write embedded software, you have to learn C/C++ (and maybe eventually Rust).
Step 2. Learn Some Basic Electronics
At least to the extent that you understand what voltage, current, power, resistance and ohms law are.
Step 3. Get the Basic Equipment
Embedded programmers interact with the physical world, so things like a soldering iron, Digital Multi-Meter (DMM) and a hardware debugger/ JTAG adapter (such as an ST-Link, or OLMEX adapter) or a Logic Analyzer would help.
Step 4. Choose a Microcontroller and Toolchain
To make your program run, you’ll need a microcontroller to actually run it, a compiler that compiles the code for the microcontroller and other tools to load the program onto your hardware. An example of the combination of microcontrollers with a toolchain is the STM32 microcontrollers that are supported by the arm-gcc along with openOCD toolchain.
Step 5. Understand the Datasheets
Before actually sitting down to write the first line of your code, you need to understand the (end user) specifications.
Step 6: Examine the Components
Analyze and pick up the components (software and hardware) required to make the product.
Step 7: Design a Product
Designing is always the most critical phase of any development cycle. The peculiarity of embedded programming is that you have to develop the hardware and software parts individually and then integrate them.
Step 8: Develop a Prototype
A prototype is a sample version created to test the concept that's developed according to the specifications using the selected hardware and software tool.
Step 9: Test the Application
Now that you have a prototype, it's possible to run test cases to tease out the potential of the application.
Step 10: Deploy the Application
After testing the application, the result is checked in a real environment to realize the Proof Of Concept – a technique used to validate an idea.
Step 11: Support and Upgrade
If needed, you should be ready to provide support and upgrade the application with new features.
<!-- wp:paragraph --> <p><span style=" />And now you're ready to start changing the world!
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

What is Software-Defined Connectivity?
Related Articles