Getting Started with MQTT Performance Testing: A Primer on Scenarios and Metrics
Getting Started with MQTT Performance Testing: A Primer on Scenarios and Metrics
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
EMQ Technologies
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



In the IoT industry, a large number of resource-constrained sensors and industrial control devices rely on unreliable and low-bandwidth networks. This reality has propelled the popularity of MQTT as an ideal IoT message transmission protocol for IoT scenarios. Consequently, it becomes crucial for MQTT brokers to ensure optimal performance and high reliability to meet the demands of IoT applications. It's essential to understand the basic testing scenarios and performance metrics before conducting a suitable test for your system. In this blog, we will give a comprehensive explanation based on the testing experience of the EMQX team, which is also applicable to all MQTT brokers testing.
"Consequently, it becomes crucial for MQTT brokers to ensure optimal performance and high reliability to meet the demands of IoT applications."
Terms Explanation
MQTT Protocol
MQTT stands for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport. Despite its name containing "message queuing," it has nothing to do with message queues. Instead, it is a lightweight messaging protocol based on a publish/subscribe model. With its simplicity, flexibility, easy implementation, support for QoS, and small message size, MQTT has become the preferred protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT).
Performance Testing
Performance Testing Performance testing is a process of using testing tools to simulate various normal, peak, or abnormal load conditions to test various performance indicators of the system under-tested. The goal is to verify whether the system can meet the user's expectations, discover performance bottlenecks in the system, and so on.
Typical MQTT Test Scenarios
There are two main test scenarios for MQTT brokers:
- Concurrent connection, including concurrent connection numbers and connection rates.
- Message throughput, including throughput for message sending and receiving, with some performance-affecting parameters, such as QoS, payload size, and topic wildcard, to simulate the production environment requirements.
The following two aspects must always be considered when designing specific performance test scenarios, especially for PoC or pre-deployment tests:
- Simulating usage scenarios in the real production environment as much as possible;
- Covering possible peak load.
Test scenarios can be subdivided into the two basic dimensions of connection and message throughput.
#1: Concurrent Connection Testing
MQTT connections are long (keep-alive) TCP connections. The client initiates a TCP connection with the MQTT broker, sends an MQTT login request, and then uses heartbeat packets to sustain the connection. In high-concurrency scenarios, establishing and maintaining long MQTT connections consumes significant resources for the broker. Through performance testing, we can measure how many concurrent connections the MQTT broker can support under limited resources.
On the other hand, the higher the connection rate (i.e., the newly established connections per second), the greater the computing resources required at the same time. It's important to consider this factor during testing, especially in scenarios where numerous devices may come online simultaneously. This value is crucial for evaluating system capacity and planning accordingly.
The third factor to consider in concurrent connection testing is whether to use TLS/SSL encrypted transmission, as it consumes additional resources. It is necessary to evaluate the degree of its impact on performance during testing.
To summarize, in MQTT concurrent connection testing, the following three scenarios should be considered:
- Gradually increase concurrent connections at a low connection rate to test system response and resource consumption. This can also determine the maximum concurrency the system can support under given hardware and network resources.
- With a fixed number of concurrent connections, test the system's response and resource consumption at different connection rates.
- Differentiate between regular TCP connections and TLS/SSL encrypted connections when designing 1) and 2).
#2: Message Throughput Testing
As mentioned earlier, MQTT is a message transfer protocol based on the publish/subscribe model. It is an asynchronous protocol that implements 1-to-1, 1-to-many, and many-to-1 types of publishing and subscription, which are widely used in various IoT scenarios. Therefore, message throughput testing should include these three scenarios:
- 1-to-1 symmetric: The number of publishers and subscribers is the same. For each publisher, there is exactly one subscriber to the published topic. In other words, the incoming messages rate is equal to the outgoing rate for the MQTT broker.
- Fan-in: A typical IoT applications scenario with many IoT devices acting as publishers, but only a few or a single subscriber, for example, a large number of devices reporting its status or data.
- Fan-out: A large number of devices subscribing to one or a few publishers.
Besides, when designing message throughput scenarios, do not forget QoS, message payload size, subscription topics with wildcards, etc. Different QoS significantly impact performance and resource consumption for load tests. The payload size can be determined based on the actual use cases.
Other Scenarios
For other MQTT functionalities, such as Shared Subscription, messages dumping to databases or MQ, a large number of topic subscriptions, and extreme situations like numerous MQTT clients connecting/disconnecting simultaneously, these can be planned and incorporated into the testing scenarios based on actual requirements.
Performance Metrics
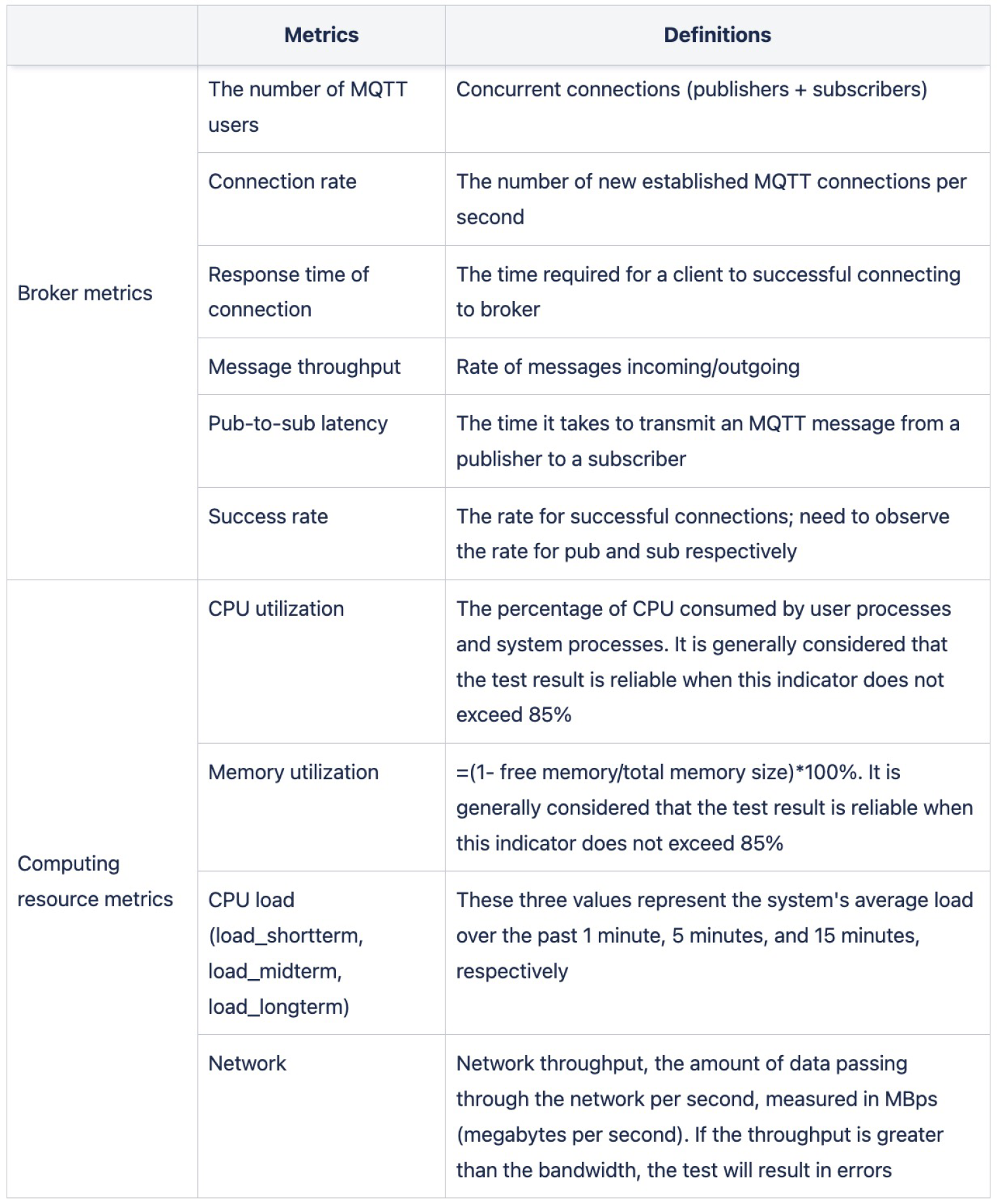
After designing a proper testing scenario, it is also important to develop performance metrics to measure the success or failure of the test. In performance testing, the metrics can generally be divided into two categories: application system metrics (here, i.e. MQTT broker metrics) and computing resource metrics.
- Application system metrics are related to user scenarios and requirements, such as response time (or latency) and concurrency.
- Computing resource metrics are related to hardware resource consumption. For MQTT we’re talking about, the metrics are similar to those of other software performance tests, such as CPU, memory, network, and disk I/O.
The MQTT system metrics are closely related to the testing scenario, and the common ones are summarized in the table below.
Wrapping up
In this post, we have discussed several typical testing scenarios and important metrics that can be used to evaluate the performance of MQTT brokers. By understanding and applying these testing techniques and metrics, you can optimize the performance and reliability, and improve the overall IoT and messaging system infrastructure.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Moving Past the Pilot Phase in IoT and AI
Related Articles