How Do IoT Businesses Benefit From Remote Device Access?
How Do IoT Businesses Benefit From Remote Device Access?
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
emnify
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



The benefits of a successful IoT solution are numerous, complementary, and wide-reaching. With all the opportunities that IoT connectivity presents, there are still security vulnerabilities, communication challenges, and logistical obstacles. Remote device access is a key ingredient in addressing these problems.
Consider Two Scenarios
- Devices are local: The IoT connectivity-enabled device is within the developer’s private network. He or she can log in to the device, read log files, run device commands, and even reset the device with the simple push of a button.
- Devices are with the customer in the field: The developer has no access to this external network. In order to troubleshoot a possible issue, he or she can only rely on the data being sent from the device, offering little to no visibility.
With all the opportunities that IoT connectivity presents, there are still security vulnerabilities, communication challenges, and logistical obstacles. Remote device access is a key ingredient in addressing these problems.
To understand the problem posed by the second scenario, imagine a malfunctioning elevator where the actions pre-programmed to resolve potential issues are simply not working. In this situation, the service personnel have no option but to physically go onsite to troubleshoot the issue, using up valuable resources.
Possible Remote Access Solutions
<!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>In the early days, businesses used static public IP addresses to log in to devices remotely much like a public webserver. However, leaving devices in the public domain makes them vulnerable to hacker attacks either via bugs or brute force password attacks. This is not dissimilar to what happened with the <a href=" />Mirai botnet attacks.
A second approach is to use private IP addresses and deploy a VPN or remote management client on each device that connects to a central server. This way, the client establishes a secure connection to a VPN server and the developer can then first log in to the central server and from there into the device itself, offering more real-time oversight.
Unfortunately, not all IoT devices possess enough processing and energy capacity to run remote client software. What’s more, managing the different VPN clients and updates is cumbersome, especially when different types of devices are involved. Meaning, this option is also less than ideal.
Preferred Solution
A better approach is to get remote device access using a virtual private network (VPN) and static private IP addresses offered by the cellular connectivity provider. This approach has many advantages including:
- The devices are hidden within the cellular provider network and no attacker can scan or send traffic towards the devices.
- The virtual private network is not built up between each device but only between the mobile network infrastructure and the VPN client of the administrator.
- The administrator can access the device by authenticating with the VPN Gateway of the mobile network so he can log in to the device.
With traditional operators this setup is time consuming, complex and expensive, because they need to setup a private APN which is required to manage the static IP addresses. The private APN had to be announced within the operator DNS and be configured in the customer device. It is not uncommon to spend several weeks and hundreds of Euros for the setup and a monthly charge for private IP addresses and the VPN.
A preferred solution is to work with a connectivity provider that delivers private static IP addresses that serve as the basis to enabling remote access, free of charge. Each SIM card would then obtain a separate private IP address without the need to setup or pay for a private APN.
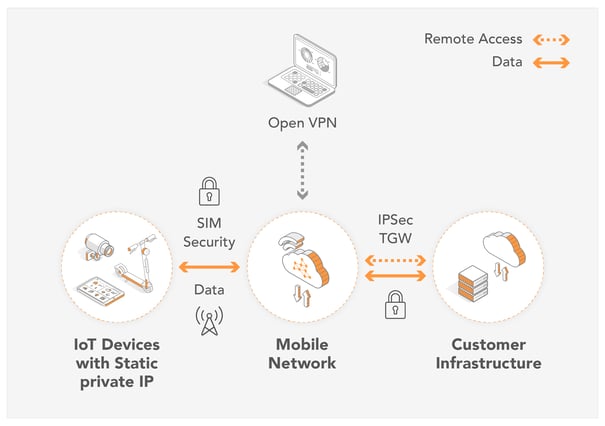
OpenVPN
By using an Open VPN client, businesses can directly access their devices from any workstation, laptop, or virtual machine. With the use of an OpenVPN client, customers can connect to a VPN Gateway, gaining access to all devices. Remote access communication between the VPN Gateway and the Laptop is encrypted.
IPSec
Businesses that wish to add an additional layer of security to their device data should use IPSec. In contrast to OpenVPN which creates a secure connection from a laptop or external device, IPSec establishes a secure connection between the application and the VPN gateway. Not only can businesses login to their devices remotely from their application infrastructure but also the device communication is encrypted on the path to the application.
Note: While it is also possible to connect the application infrastructure to the mobile network using OpenVPN - this is not recommended. OpenVPN has a maximum bandwidth limitation of about 20 Mbps that all devices share and can impact device operation. Furthermore, with OpenVPN, the routing is only done to one IP address, whereas IPSec is to the full application subnet.
Summary
Remote access is a key ingredient for any successful IoT solution that is deployed remotely. From a security perspective, it is advisable to use private IP addresses to enable remote access, instead of relying on public internet. A basic option offers remote access through OpenVPN. For additional device and infrastructure security, IPSec or Cloud Connect also provide encryption of the data path.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

What is Software-Defined Connectivity?
Related Articles